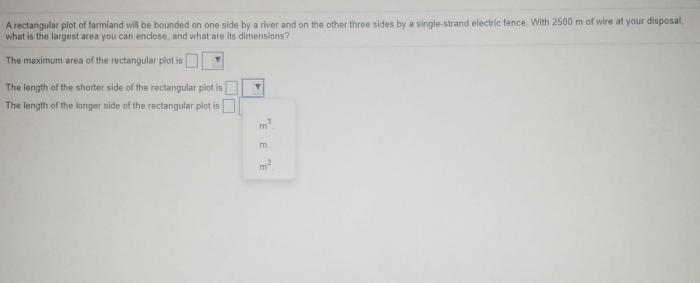
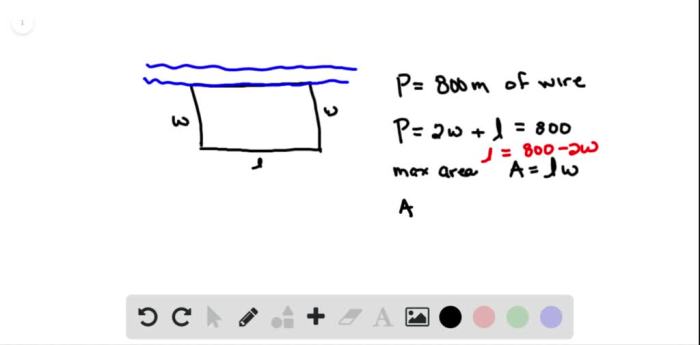
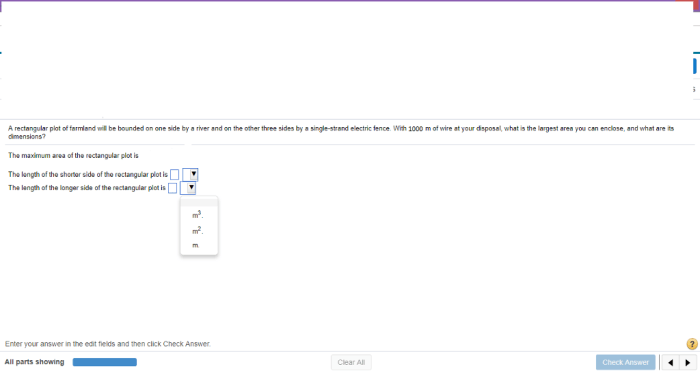
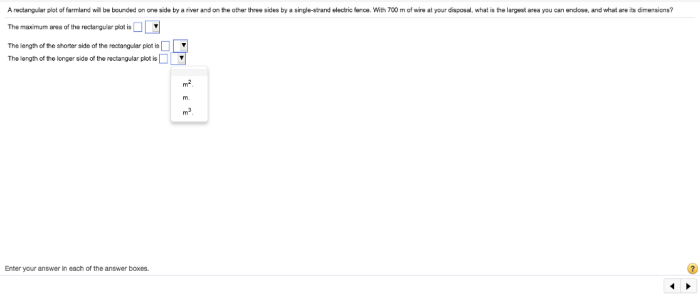
A rectangular plot of farmland will be bounded – Rectangular plots of farmland, defined by their distinct boundaries, present unique opportunities and challenges for land management. This comprehensive guide delves into the concept of rectangular plots, exploring their implications for perimeter and area calculations, land utilization, fencing and boundary markings, access and infrastructure, and environmental considerations.
With a focus on practical applications, this guide provides formulas for calculating the perimeter and area of rectangular plots, discussing the relationship between these measurements. It examines how the shape of a rectangular plot influences land utilization and offers strategies for optimizing land use within these defined boundaries.
Rectangular Plot Boundary: A Rectangular Plot Of Farmland Will Be Bounded
A rectangular plot of farmland is a two-dimensional area defined by four straight sides that form right angles at each corner. The term “bounded” in this context refers to the establishment of clear and defined limits for the plot, ensuring its separation from surrounding areas.
Having a rectangular plot with defined boundaries provides several advantages. It simplifies land management, prevents encroachment, and facilitates accurate measurements for agricultural operations.
Perimeter and Area Calculations
The perimeter of a rectangle is the total length of its boundary, calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides. The formula for perimeter is: P = 2(length + width)
The area of a rectangle is the amount of two-dimensional space enclosed within its boundaries. The formula for area is: A = length × width
These formulas are essential for determining the size and dimensions of the rectangular plot and for calculating the amount of fencing required to secure its perimeter.
Land Utilization and Optimization
The rectangular shape of the plot influences how land can be utilized for agricultural purposes. Rectangular plots allow for efficient and organized crop planting, with rows or columns aligned in straight lines.
Strategies for optimizing land use within a rectangular plot include:
- Planning crop rotations to maximize soil health and prevent disease buildup.
- Using raised beds or terraces to improve drainage and increase growing space.
- Implementing precision farming techniques to optimize resource allocation and minimize waste.
Fencing and Boundary Markings
Fencing is essential for securing the perimeter of the rectangular plot and preventing unauthorized access or encroachment. Common fencing options include:
- Barbed wire fences:Cost-effective and effective deterrent against livestock and trespassers.
- Woven wire fences:More durable and aesthetically pleasing, suitable for a variety of purposes.
- Electric fences:Provide a non-lethal way to deter animals and intruders.
Boundary markings, such as stakes or posts, are crucial for clearly defining the plot’s limits and preventing disputes or encroachment.
Access and Infrastructure, A rectangular plot of farmland will be bounded
Access points to the plot are essential for agricultural operations, equipment movement, and transportation of goods. Considerations for access design include:
- Gates:Provide controlled access to the plot while preventing unauthorized entry or exit.
- Roads:Allow for easy movement of vehicles and equipment within the plot.
- Bridges or culverts:Enable access across waterways or uneven terrain.
Proper planning and design of access infrastructure ensure efficient and functional operations within the plot.
Environmental Considerations
The rectangular plot can have an impact on the surrounding environment. Considerations for mitigating environmental risks include:
- Erosion control:Implement measures such as contour plowing, terracing, or vegetation cover to prevent soil erosion.
- Soil management:Practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and mulching improve soil health and reduce nutrient runoff.
- Water management:Install drainage systems or water retention structures to prevent waterlogging or flooding.
By addressing environmental concerns, farmers can ensure the long-term sustainability of the rectangular plot and minimize its impact on the ecosystem.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the implications of having a rectangular plot with defined boundaries?
Rectangular plots with defined boundaries simplify perimeter and area calculations, facilitate efficient land utilization, and provide a clear framework for fencing and boundary markings.
How can I optimize land use within a rectangular plot?
Strategies for optimizing land use include crop rotation, companion planting, vertical gardening, and efficient layout planning to maximize space utilization.
What are the legal considerations related to fencing and boundary maintenance?
Legal considerations include adhering to local zoning regulations, obtaining necessary permits, and establishing clear boundary lines to prevent encroachment.