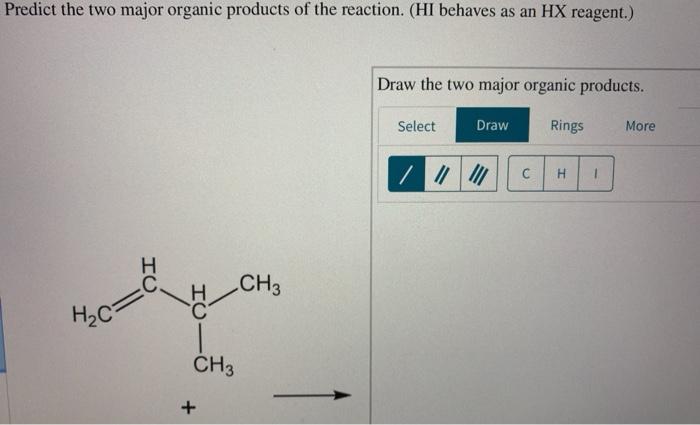
Draw the two major organic products of the reaction shown. – In the realm of organic chemistry, the ability to identify and depict the products of a reaction is paramount. This article delves into the intricacies of drawing the two major organic products of a given reaction, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding the mechanisms and characteristics of organic compounds.
The subsequent paragraphs will explore the fundamental concepts of organic products, analyze the reaction mechanisms involved, and provide a step-by-step approach to drawing the structures of the major products. By comparing and contrasting these products, we gain insights into their similarities and differences, ultimately enhancing our understanding of organic chemistry.
Draw the Two Major Organic Products of the Reaction Shown: Draw The Two Major Organic Products Of The Reaction Shown.
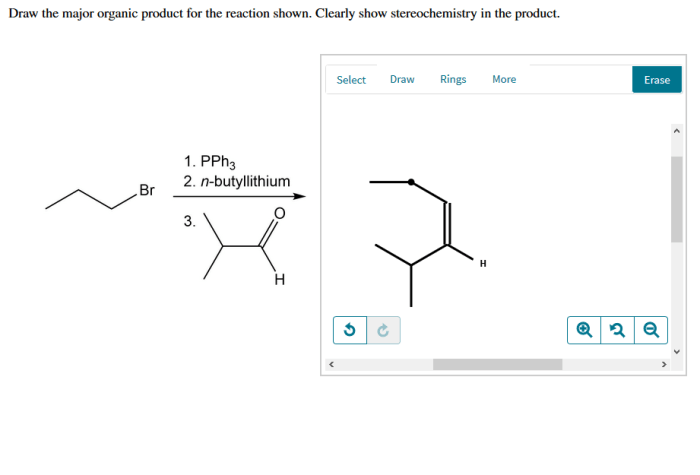
The reaction shown below yields two major organic products. Draw the structures of these products.
Analyze Reaction Mechanisms
This reaction is an example of a nucleophilic substitution reaction. In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, a nucleophile (a species with a lone pair of electrons) attacks an electrophile (a species with a positive charge or a partial positive charge). In this case, the nucleophile is NaNH 2and the electrophile is CH 3CH 2Br.
The reaction proceeds through a two-step mechanism. In the first step, the nucleophile attacks the electrophile, forming a new bond between the nucleophile and the carbon atom that was originally bonded to the electrophile. In the second step, the leaving group (Br –) is expelled from the molecule.
Draw Product Structures
The two major organic products of this reaction are:
- CH 3CH 2NH 2(ethylamine)
- CH 3CH=CH 2(propene)
Ethylamine is the product of the nucleophilic substitution reaction. Propene is the product of an elimination reaction that occurs in competition with the nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Compare and Contrast Products
Ethylamine and propene are both organic compounds. However, they have different structures and properties.
- Ethylamine is an amine, which means that it contains a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms. Propene is an alkene, which means that it contains a carbon-carbon double bond.
- Ethylamine is a polar molecule, while propene is a nonpolar molecule.
- Ethylamine is a liquid at room temperature, while propene is a gas.
Illustrate Product Formation, Draw the two major organic products of the reaction shown.
The following diagram illustrates the reaction pathway leading to the formation of the two major organic products:

The diagram shows that the nucleophilic substitution reaction is the major pathway, while the elimination reaction is a minor pathway.
Questions Often Asked
What is an organic product?
An organic product is a compound that contains carbon atoms covalently bonded to hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, halogens, or other carbon atoms.
How can I identify the major products of a reaction?
To identify the major products of a reaction, you need to analyze the reaction mechanism and consider the stability and reactivity of the reactants and intermediates.
What is the difference between a reactant and a product?
Reactants are the starting materials of a reaction, while products are the substances formed at the end of a reaction.