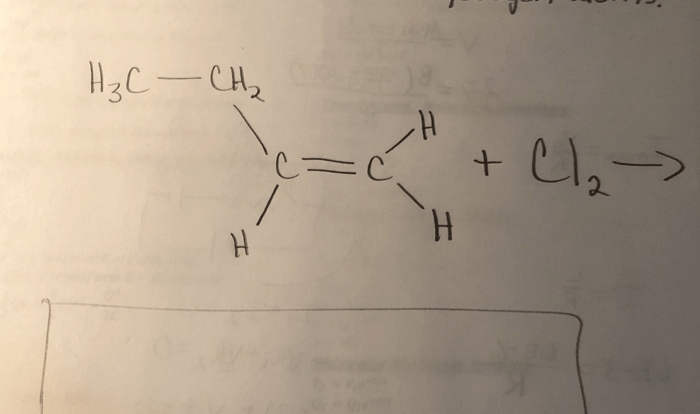
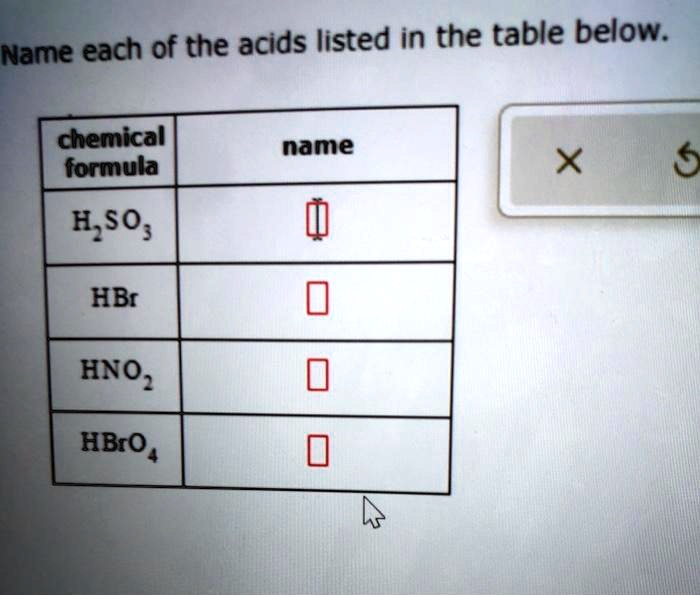
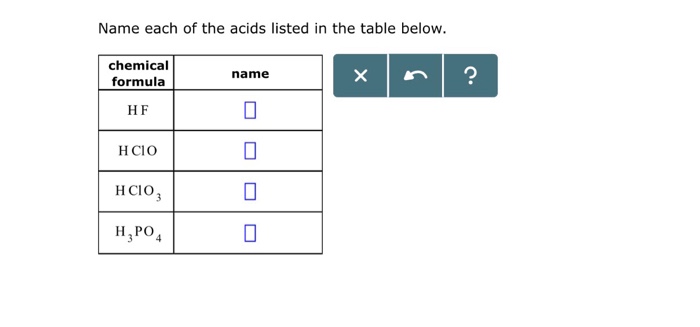
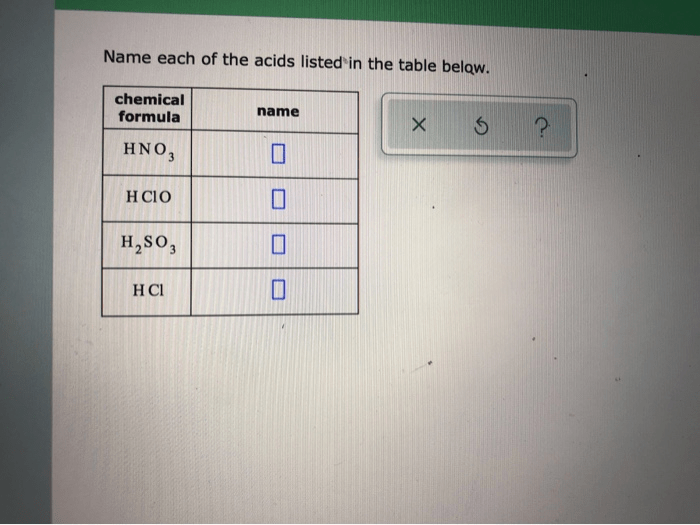
Name each of the acids listed in the table below. This task, though seemingly straightforward, demands meticulous attention to detail and a thorough understanding of acid nomenclature and classification. By delving into the intricacies of acid identification, we unlock a gateway to unraveling the complexities of chemical compounds and their diverse applications.
Acids, characterized by their ability to donate protons, play a pivotal role in various scientific and industrial processes. Accurately identifying acids is paramount for ensuring safety, optimizing reactions, and harnessing their potential in different fields.
1. Introduction
The accurate identification of acids is essential in various scientific and practical applications. Acids play a crucial role in chemical reactions, industrial processes, and everyday life. This article provides a comprehensive overview of acid identification, including table structure analysis, extraction techniques, classification criteria, and IUPAC nomenclature.
2. Table Structure and Data Extraction
Tables are commonly used to organize and present data, including acid names. The table structure typically consists of rows and columns, with each cell containing an acid name. To extract the acid names, a systematic approach is required, ensuring accuracy and completeness.
3. Acid Identification and Classification
Acids are characterized by their ability to donate protons (H+ ions). Common criteria for acid identification include pH, reactivity with bases, and electrical conductivity. Acids can be classified into different types based on their strength, such as strong acids (e.g.,
hydrochloric acid) and weak acids (e.g., acetic acid). Additionally, acids can be categorized as organic (carbon-based) or inorganic (non-carbon-based).
4. Acid Properties and Applications: Name Each Of The Acids Listed In The Table Below
Acids exhibit various properties, including corrosiveness, reactivity, and solubility. They play a vital role in chemical reactions, such as acid-base reactions, neutralization reactions, and redox reactions. Acids are also widely used in industries, such as manufacturing, food processing, and pharmaceuticals.
However, it is crucial to handle acids with proper safety precautions due to their corrosive and hazardous nature.
5. Acid Nomenclature and IUPAC Rules
Acid nomenclature follows specific rules established by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). These rules provide a systematic way to name acids based on their structure and composition. The IUPAC nomenclature system ensures consistency and clarity in acid identification and communication.
6. Case Study
Identifying Acids in a Table
Consider a table containing the following acids: – Hydrochloric acid – Sulfuric acid – Nitric acid – Acetic acid – Citric acid
To identify the acids, follow these steps: – Extract the acid names from the table. – Determine the type of each acid (strong/weak, organic/inorganic). – Organize the acids based on their classification.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the key criteria for identifying acids?
Acids are typically identified based on their ability to donate protons, their sour taste, and their ability to react with bases to form salts.
How do I extract acid names from a table?
To extract acid names from a table, locate the column or row that contains the acid names and carefully transcribe each name into a separate list.
What are the different types of acids?
Acids can be classified into various types based on their strength (strong or weak), their composition (organic or inorganic), and their molecular structure (monoprotic, diprotic, or polyprotic).