Embark on an educational journey with our comprehensive Polygons and Quadrilaterals Unit Test. This assessment will challenge your understanding of these geometric shapes, their properties, and their practical applications. Prepare to demonstrate your knowledge and solidify your grasp of this essential geometry topic.
Delve into the realm of polygons and quadrilaterals, where you will explore their definitions, classifications, and the formulas used to calculate their area and perimeter. Discover the unique properties of specific quadrilaterals, such as squares, rectangles, parallelograms, and trapezoids. Understand how to identify and classify these shapes based on their characteristics.
Polygons and Quadrilaterals: Definitions and Classifications
Polygons are closed figures formed by straight lines. Quadrilaterals are polygons with four sides. Polygons can be classified based on the number of sides they have, while quadrilaterals can be classified based on the length of their sides and the angles between them.
Examples of polygons include triangles (3 sides), squares (4 sides), pentagons (5 sides), and hexagons (6 sides). Examples of quadrilaterals include squares (4 equal sides, 4 right angles), rectangles (4 equal sides, 2 pairs of parallel sides), parallelograms (4 sides, 2 pairs of parallel sides), and trapezoids (1 pair of parallel sides).
Properties of polygons include the sum of the interior angles being (n-2) – 180 degrees, where n is the number of sides. Properties of quadrilaterals include opposite sides being parallel and opposite angles being equal.
Area and Perimeter of Polygons and Quadrilaterals
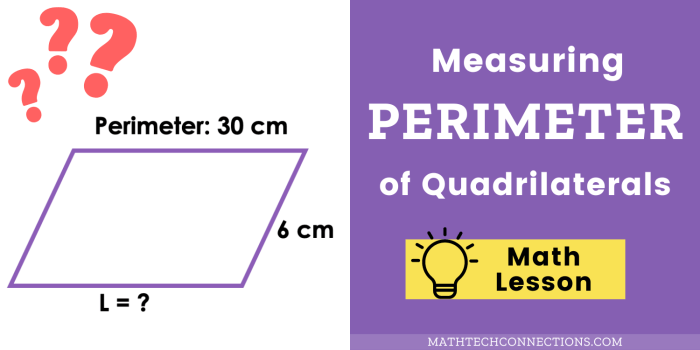
The area of a polygon is the amount of space it encloses. The perimeter of a polygon is the distance around its edges.
The area of a rectangle is calculated as length – width. The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated as 2 – (length + width).
The area of a triangle is calculated as 0.5 – base – height. The perimeter of a triangle is calculated as the sum of the lengths of its three sides.
Properties of Specific Quadrilaterals: Polygons And Quadrilaterals Unit Test
Squares
- All sides are equal.
- All angles are right angles (90 degrees).
- Diagonals are equal and bisect each other.
Rectangles, Polygons and quadrilaterals unit test
- Opposite sides are equal.
- Opposite angles are equal.
- Diagonals are equal.
Parallelograms
- Opposite sides are parallel.
- Opposite angles are equal.
Trapezoids
- One pair of opposite sides is parallel.
- Non-parallel sides are called legs.
- Bases are the parallel sides.
Transformations of Polygons and Quadrilaterals
Transformations are operations that can be applied to polygons and quadrilaterals to change their position, size, or shape.
Translations
Translations move a polygon from one point to another without changing its size or shape.
Rotations
Rotations turn a polygon around a fixed point.
Reflections
Reflections flip a polygon over a line.
Applications of Polygons and Quadrilaterals
Polygons and quadrilaterals are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Architecture: Polygons and quadrilaterals are used to design buildings, bridges, and other structures.
- Engineering: Polygons and quadrilaterals are used to design machines, vehicles, and other products.
- Design: Polygons and quadrilaterals are used to create logos, artwork, and other designs.
FAQ Compilation
What is the difference between a polygon and a quadrilateral?
A polygon is any closed figure with straight sides, while a quadrilateral is a specific type of polygon with four sides.
How do I calculate the area of a rectangle?
Multiply the length by the width of the rectangle.
What is the formula for the perimeter of a square?
Multiply the length of one side by 4.
How can I identify a parallelogram?
A parallelogram has opposite sides that are parallel and equal in length.